compose-a-tetris 使用 compose API 在安卓上实现一个俄罗斯方块
写在前面
为了应付安卓课的大作业,又写了一个俄罗斯方块。很幸运的是,确实学到了很多知识,虽然这些知识可能没什么用,但是还是非常的有意思。上一次写俄罗斯方块是高三的时候是在 hp-39gii 图形机上拿着简陋的 hp-basic 写的,最后写出来的结果是这样的
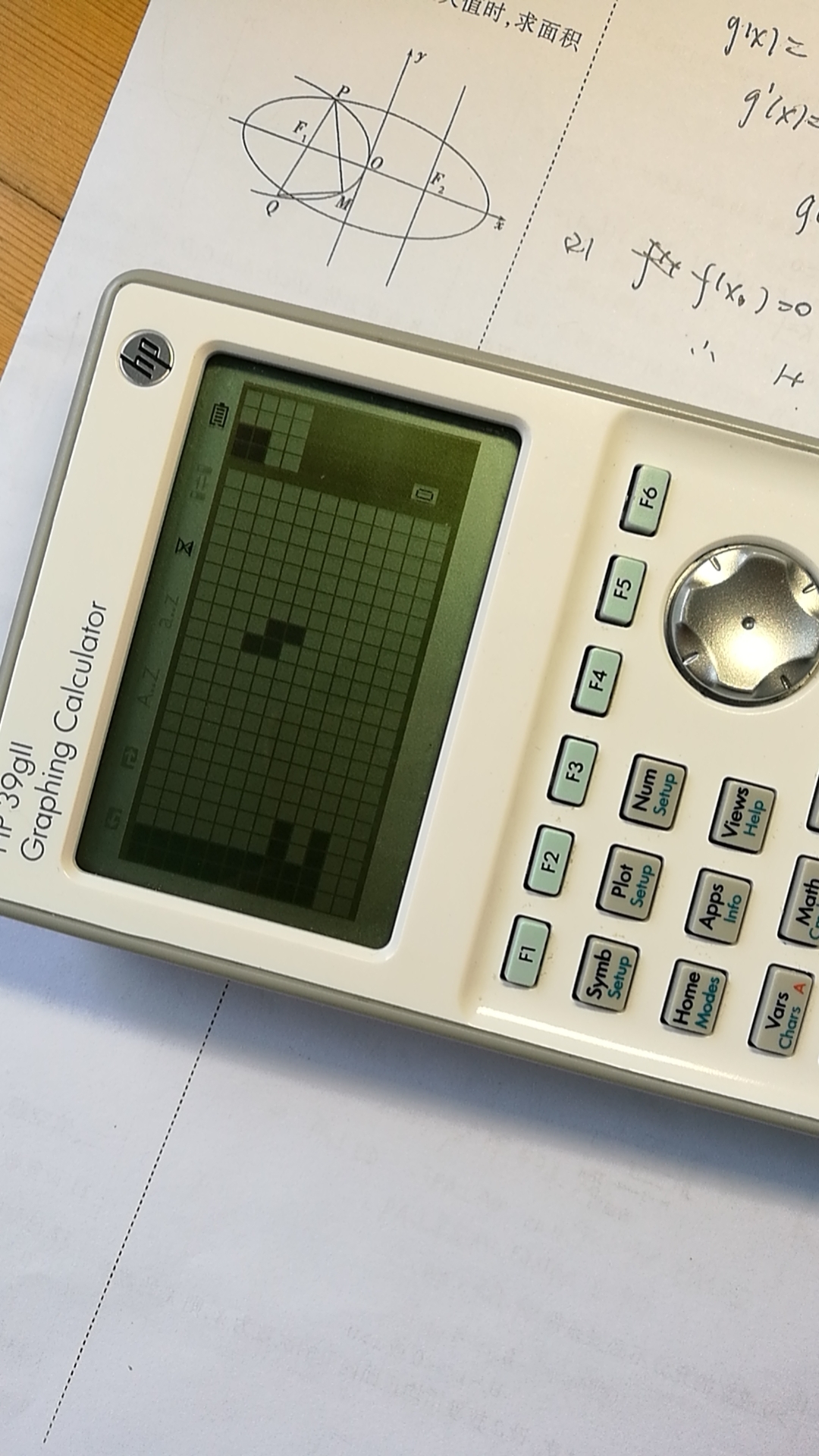

遗憾的是当时的源代码已经丢失了,编译后的字节码倒还是在,重新导入回计算器还能把源码找回来,但是我已经懒得折腾这个了,属于是时代的眼泪了。
话说回来,这学期选了一节安卓移动开发的专业选修课,当时是有打算入门一下安卓,之后浏览器或者内核安全研究不下去了,也可以试试移动安全。不过上了课发现这课主要的可能还是偏向于让我们能写出来一个 app,而不是了解安卓的思想。学到的东西也是 api 怎么用,gui 怎么调。不能说没意思吧,其实做点实际的东西出来还是很有成就感的。期末作业有许多选择,都不太感兴趣。然后正好看到这篇文章:用Jetpack Compose做一个俄罗斯方块游戏机,我也不知道 jetpack 或者 compose 是什么,里面还提到了 MVI 架构,都是没接触过的名词,为了学习也好,为了以后吹牛皮也好,为了抄起来方便也好,我就选择了拿 compose 写俄罗斯方块这个作业。真的非常感谢这位作者:),我吹爆!
功能实现方面呢,参考的文章里面只实现了一个很炫酷的游戏界面,课程的要求为了让我们涉及更多的东西,还要求要做到
- 只能有五种方块,这个好解决,生成的时候限制一下范围就行
- 需要能把分数存到数据库里面
- 需要能够按名称和按起止时间搜索记录
- 挂了之后要能播放音乐
首先照着文章抄,把游戏主体逻辑实现了,这里我花的时间最少,(绝对不是因为有的抄!),俄罗斯方块这个游戏的特点就是不断地等待用户输入,输入了之后渲染界面(spirit 会持续下落,也可以理解为是用户的输入),这种模型据说非常符号前端的开发思想,数据驱动。
MVI
这里使用的主要就是 MVI 架构了,即
- Model:主要指 UI 的状态。UI 本质就是一堆控件分布在各个位置上。我们稍微抽象一下就可以把 UI 状态存到一个数据类中,我们称之为一个 state。
- View:与 MV* 中的 View 一样,指任意一个 Activity、Fragment 等 UI 承载单元。在这个项目中,使用了 compose 这套较新的 API,其自动、智能重组的特性也很适合做 View 层。
- Intent:这个 intent 指的是用户的操作的意图(和 Activity 中的那个 Intent 不是一个东西)。把它封装到一个 Action 中再发送给 Model 进行数据请求(一次 reduce 操作)。
这个架构模式满足单向数据流,整个流向如下
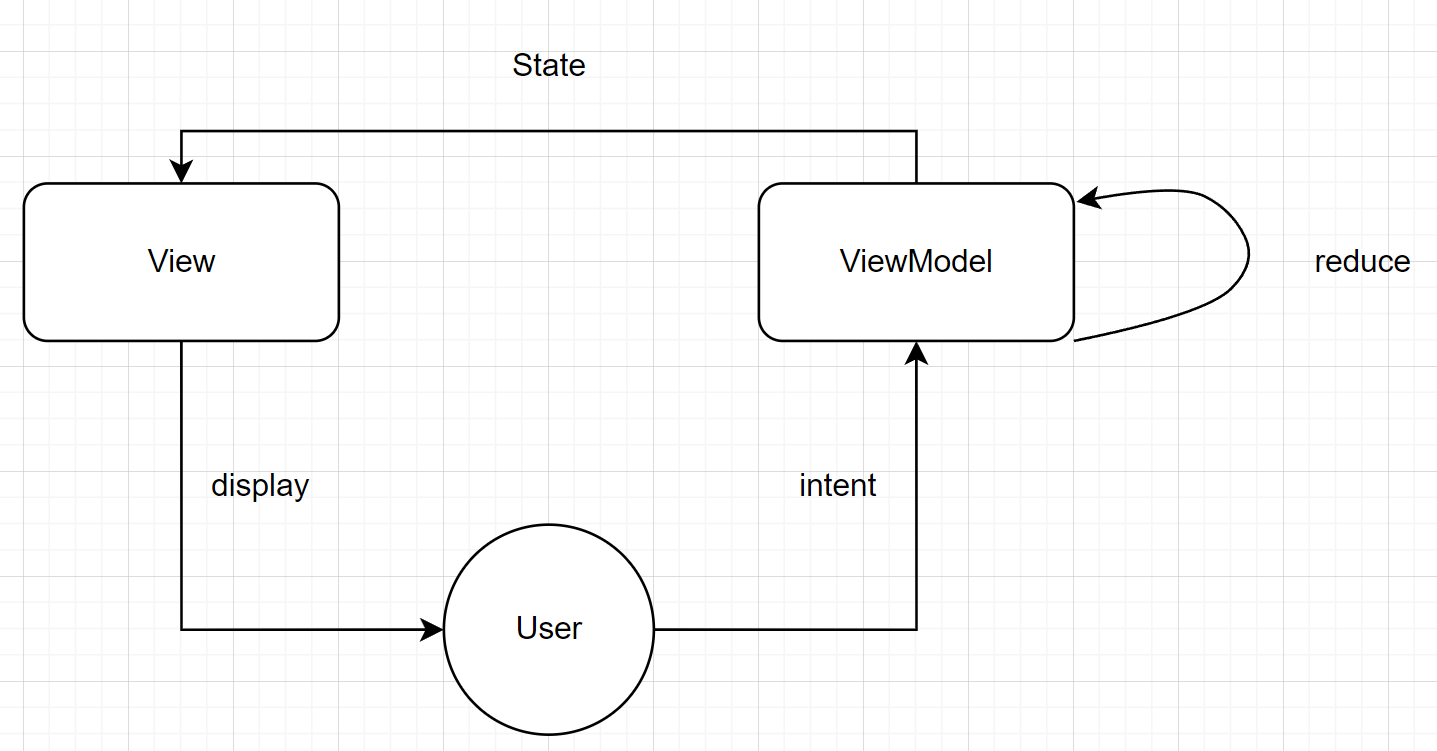
也就是说流程为:用户输入封装为 intent 发送给 ViewModel,ViewModel 根据 intent 进行 reduce 更新 state,View 根据 state 刷新 UI,再显示给用户。
抄下一下网络上总结的架构优缺点
优点:
- UI的所有变化来自State,所以只需聚焦State,架构更简单、易于调试
- 数据单向流动,很容易对状态变化进行跟踪和回溯
- state实例都是不可变的,确保线程安全
- UI只是反应State的变化,没有额外逻辑,可以被轻松替换或复用
缺点:
- 所有的操作最终都会转换成State,所以当复杂页面的State容易膨胀
- state是不变的,每当state需要更新时都要创建新对象替代老对象,这会带来一定内存开销
- 有些事件类的UI变化不适合用state描述,例如弹出一个 toast 或者 snackbar
安卓为开发者提供了非常多的基础类,让 MVI 的实现变得十分容易,接下来我以此俄罗斯方块项目为例展示一下。
View
首先来实现 view 层,这里使用 compose 这个函数式、声明式的 api。
先实现一个方块的绘制
// this function can draw a single Brick
// to a single Brick, there is there part
// |--------|
// ||------||
// |||----|||
// ||| |||
// |||----|||
// ||------||
// |--------|
// 1.0 0.8 0.5
// here we should draw the inner two part
// named inner part and outer part
private fun DrawScope.drawBrick(
brickSize : Float,
relativeOffset : Offset,
color : Color
) {
val location = Offset(
relativeOffset.x * brickSize,
relativeOffset.y * brickSize
)
val outerSize = brickSize * 0.8f
val outerOffset = (brickSize - outerSize) / 2f
drawRect(
color = color,
topLeft = location + Offset(outerOffset, outerOffset),
size = Size(outerSize, outerSize),
style = Stroke(outerSize / 10f)
)
val innerSize = brickSize * 0.5f
val innerOffset = (brickSize - innerSize) / 2f
drawRect(
color = color,
topLeft = location + Offset(innerOffset, innerOffset),
size = Size(innerSize, innerSize),
)
}
preview 出来看看
@Preview(showBackground = true)
@Composable
fun BrickPreview() {
Canvas(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
drawBrick(size.width, Offset(0f, 0f), Color.Green)
}
}
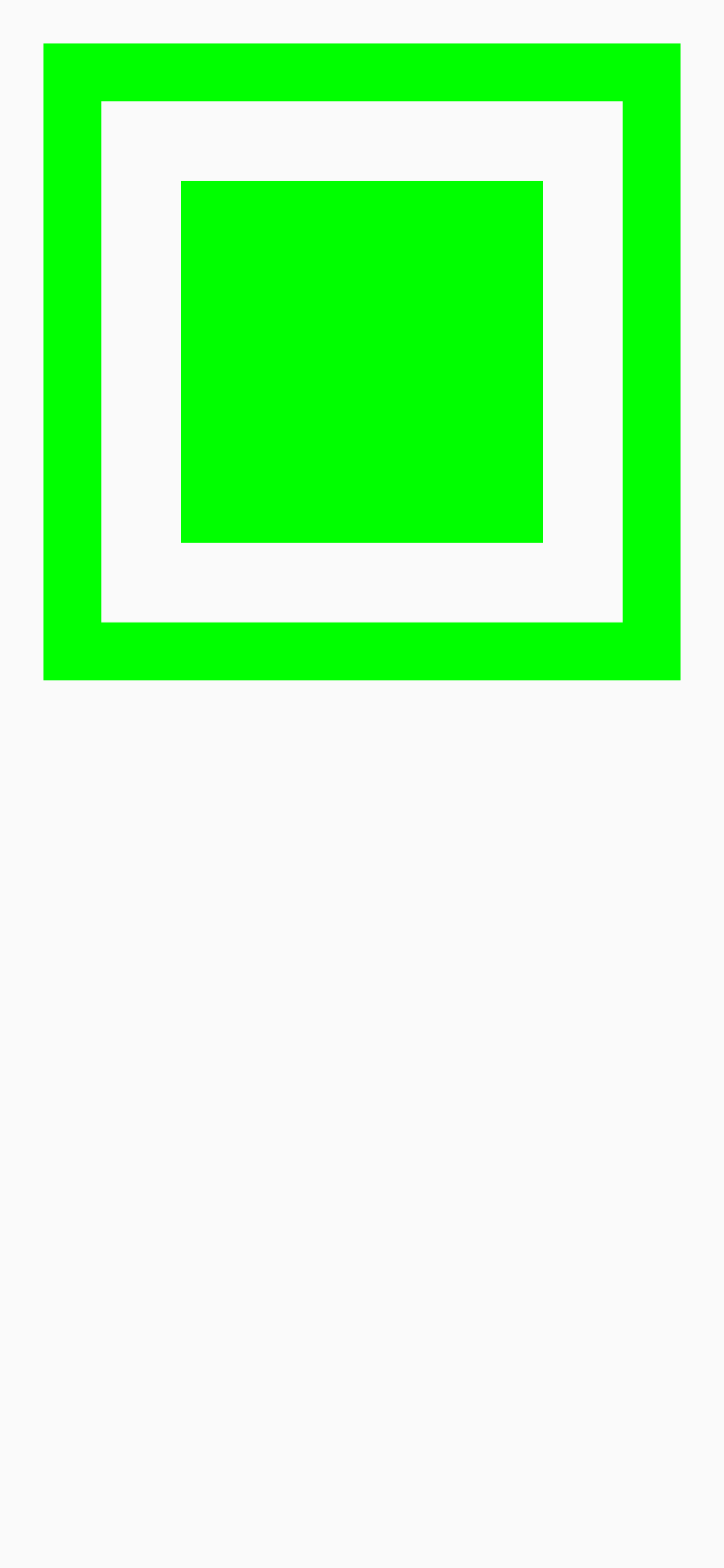
效果不错。compose 的一大优点就是能够实时预览 UI 形状,效果和真机的差距也不是很大。
然后把整个背景板画出来
fun DrawScope.drawGrid(
blockSize : Float,
gridSize : Pair<Int, Int>
) {
(0 until gridSize.first).forEach { x ->
(0 until gridSize.second).forEach { y ->
drawBrick(
blockSize,
Offset(x.toFloat(), y.toFloat()),
BrickGrid
)
}
}
}
preview 一下效果如下
然后我们定义所有的下落方块(spirit)的形状,形状通过一个 Offset 链表描述
val SpiritType = listOf(
listOf(Offset(1f, -1f), Offset(1f, 0f), Offset(0f, 0f), Offset(0f, 1f)),//Z
listOf(Offset(0f, -1f), Offset(0f, 0f), Offset(0f, 1f), Offset(0f, 2f)),//I
listOf(Offset(0f, 1f), Offset(0f, 0f), Offset(0f, -1f), Offset(1f, 0f)),//T
listOf(Offset(1f, 0f), Offset(0f, 0f), Offset(1f, -1f), Offset(0f, -1f)),//O
listOf(Offset(1f, -1f), Offset(0f, -1f), Offset(0f, 0f), Offset(0f, 1f)),//J
// here starts the unwanted
listOf(Offset(0f, -1f), Offset(1f, -1f), Offset(1f, 0f), Offset(1f, 1f)),//L
listOf(Offset(0f, -1f), Offset(0f, 0f), Offset(1f, 0f), Offset(1f, 1f)),//S
)
课程的作业要求只能有前五种方块,很好解决,生成的时候限制一下随机数的范围即可。然后定义一下他们的颜色
val SpiritColor = listOf(
Color.Blue,
Color.Red,
Color.Yellow,
Color.Green,
Color.Magenta,
Color.Cyan,
Color.Black
)
实现 spirit 的绘制
fun DrawScope.drawSpirit(spirit: Spirit, brickSize: Float, gridSize: Pair<Int, Int>) {
clipRect(0f, 0f, gridSize.first * brickSize, gridSize.second * brickSize) {
spirit.location.forEach {
drawBrick(
brickSize,
it,
spirit.color
)
}
}
}
遍历一遍链表就可以了。
然后我们把三者结合起来
@Composable
fun GridScreen(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
val viewModel = viewModel<GameViewModel>()
val viewState = viewModel.viewState.value
Box(
modifier = modifier
.background(Color.White)
) {
Canvas(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
val brickSize = min(
size.width / viewState.grid.first,
size.height / viewState.grid.second)
drawGrid(blockSize = brickSize, gridSize = viewState.grid)
drawSpirit(
spirit = viewState.spirit,
brickSize = brickSize,
gridSize = viewState.grid)
drawBricks(brickSize = brickSize, bricks = viewState.bricks)
}
}
}
注意开头取得了 viewModel。我没有深究过其实现,因为不懂 Java,kotlin 对我来说更像是黑魔法。不过大概能猜出来大概是一个单例+被观察者(即主题)。编译器可能会做点什么操作让这个函数自动变成一个 observer,然后每当 viewModel 改变的时候都会重新调用这个函数(也就是进行 compose 中的重组)。这里也能感受到 kotlin 真的是一个很方便的语言,很多设计模式都隐藏好了,甚至已经做到了对开发者透明(代价就是不知道他到底做了什么,让人感觉就是某种黑魔法)。这样 view 层基本完事了,还差一些按钮来与用户交互,首先定义一个 clickable 类,描述所有的可点击操作
data class Clickable constructor(
val onMove: (Direction) -> Unit,
val onRotate: () -> Unit,
val onPause: () -> Unit,
val onReset: () -> Unit,
val onExit: () -> Unit,
)
fun combineClickable (
onMove: (Direction) -> Unit = {},
onRotate: () -> Unit = {},
onPause: () -> Unit = {},
onReset: () -> Unit = {},
onExit: () -> Unit = {},
) = Clickable(onMove, onRotate, onPause, onReset, onExit)
然后绘制出“状态改变按钮”,并注册相应的 onClick 方法
@Composable
fun GameStateController(
clickable: Clickable = combineClickable(),
modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
Box(modifier = modifier
.padding(5.dp)
.width(StateButtonWidth * 3f * 1.5f)
.height(StateButtonHeight)
) {
Button(
onClick = clickable.onPause,
modifier = Modifier
.align(Alignment.Center)
.height(StateButtonHeight)
.width(StateButtonWidth)
) {
Text(
text = stringResource(id = R.string.button_pause_str),
fontSize = 10.sp
)
}
Button(
onClick = clickable.onReset,
modifier = Modifier
.align(Alignment.CenterStart)
.height(StateButtonHeight)
.width(StateButtonWidth)
) {
Text(
text = stringResource(id = R.string.button_reset_str),
fontSize = 12.sp
)
}
Button(
onClick = clickable.onExit,
modifier = Modifier
.align(Alignment.CenterEnd)
.height(StateButtonHeight)
.width(StateButtonWidth)
) {
Text(
text = stringResource(id = R.string.button_exit_str),
fontSize = 12.sp
)
}
}
}
再绘制出方向键
@Composable
fun DirectionButtonAssembly(
directionButtonSize : Dp,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
onMove: (Direction) -> Unit = {}
) {
val buttonText = @Composable {
textModifier : Modifier,
text : String ->
Text(
text = text,
color = Color.White,
fontSize = 25.sp,
modifier = textModifier
)
}
Box(modifier = modifier.size(directionButtonSize * 2.5f)
) {
BasicButton(
modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.TopCenter),
size = directionButtonSize,
onClick = { onMove(Direction.Up) }
) {
buttonText(it.align(Alignment.Center), stringResource(id = R.string.button_up_str))
}
BasicButton(
modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.CenterStart),
size = directionButtonSize,
onClick = { onMove(Direction.Left) }
) {
buttonText(it, stringResource(id = R.string.button_left_str))
}
BasicButton(
modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.CenterEnd),
size = directionButtonSize,
onClick = { onMove(Direction.Right) }
) {
buttonText(it, stringResource(id = R.string.button_right_str))
}
BasicButton(
modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.BottomCenter),
size = directionButtonSize,
onClick = { onMove(Direction.Down) }
) {
buttonText(it, stringResource(id = R.string.button_down_str))
}
}
}
还有 Rotate
@Composable
fun RotateButton(rotateButtonSize : Dp, modifier: Modifier, onRotate: () -> Unit = {}) {
BasicButton(
modifier = modifier,
size = rotateButtonSize,
onClick = onRotate
) {
Text(
text = stringResource(id = R.string.button_rotate_str),
color = Color.White,
fontSize = 22.sp,
modifier = it
)
}
}
@Composable
fun GameMoveController(
clickable: Clickable = combineClickable(),
modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
Box(modifier = modifier
.width(DirectionButtonSize * 2.5f + RotateButtonSize * 1.5f)
.height(DirectionButtonSize * 2.5f)
) {
DirectionButtonAssembly(
directionButtonSize = DirectionButtonSize,
modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.CenterStart),
onMove = clickable.onMove
)
RotateButton(
rotateButtonSize = RotateButtonSize,
modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.CenterEnd),
onRotate = clickable.onRotate
)
}
}
还有一些对于分数、下一个 spirit 的绘制,这里不一一赘述了,最后的 preview 是这样
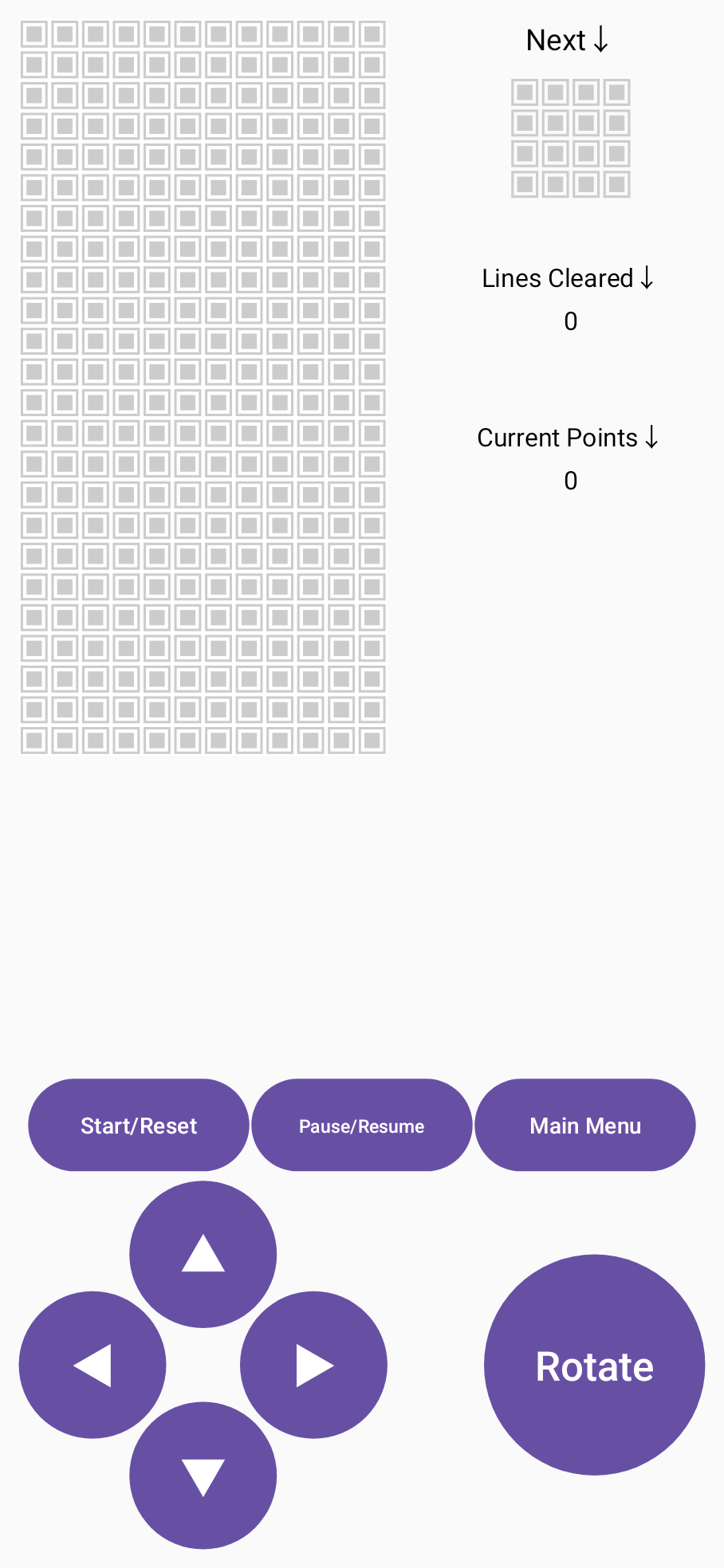
ViewModel
然后我们实现 viewModel。首先定义 UI 样式的 state
data class ViewState(
val bricks : List<Brick> = emptyList(),
val spirit: Spirit = Empty,
val nextSpirit : Spirit = Empty,
val grid : Pair<Int, Int> = GridWidth to GridHeight,
val gameStatus : GameStatus = GameStatus.OnBoard,
val score : Int = 0,
val linesCleared : Int = 0,
) {
val isRunning
get() = gameStatus == GameStatus.Running
val isPaused
get() = gameStatus == GameStatus.Paused
val isOnBoard
get() = gameStatus == GameStatus.OnBoard
val isGameOver
get() = gameStatus == GameStatus.GameOver
val isOnGameOverAnimation
get() = gameStatus == GameStatus.OnGameOverAnimation
}
然后在 viewModel 里面存上这个 mutableState
class GameViewModel : ViewModel() {
private val _viewState : MutableState<ViewState> = mutableStateOf(ViewState())
val viewState : State<ViewState> = _viewState
暴露出一个只读的 viewState 让 UI 层读取。
然后只要实现 reduce 方法来更新数据就可以了
fun dispatch(action: Action) {
_viewState.value = reduce(viewState.value, action)
}
private fun reduce(state: ViewState, action: Action): ViewState =
when(action) {
Action.Reset -> {
...
}
Action.Move -> {
...
}
...
}
具体代码这里就不放了,俄罗斯方块的底层逻辑不在我们的讨论范围内
然后就可以写出所有的 click 方法了
combineClickable (
onMove = {direction : Direction ->
if(direction == Direction.Up) viewModel.dispatch(Action.DropImm)
else viewModel.dispatch(Action.Move(direction))
},
onReset = {
viewModel.dispatch(Action.Reset)
},
onRotate = {
viewModel.dispatch(Action.Rotate)
},
onPause = {
viewModel.dispatch(Action.Pause)
},
onExit = {
// go the main activity
val intent = Intent(context, MainActivity::class.java)
context.startActivity(intent)
}
Intent
这里 intent 就比较简单了,一个 action 即可描述
sealed interface Action {
data class Move(val direction: Direction) : Action
object Reset : Action
object Pause : Action
object Rotate : Action
object DropImm : Action
object Exit : Action
object Tick: Action
}
其他主题
MVI 到这里就结束了,这个俄罗斯方块写到这里就可以跑了。不过之后还有一些别的需求,这里就没有代码可以参考了,我们一个个来讨论
分数存储
首先挂的时候,弹一个 alert 出来要求用户输入名字,这个 alert 在 jetpack compose 中也有,也就是 AlertDialog
@Preview(showBackground = true)
@Composable
fun GameOverAlert() {
val context = LocalContext.current
val openDialog = remember { mutableStateOf(true) }
val viewModel = viewModel<GameViewModel>()
val viewState = viewModel.viewState.value
val userName = remember { mutableStateOf("") }
val dbHelper = ScoreDBHelper(context)
if (openDialog.value) {
AlertDialog(
onDismissRequest = {
openDialog.value = false
},
title = {
Text(text = GAME_OVER_ALERT_TITLE)
},
text = {
Column {
Text(text = INPUT_NAME_HINT)
TextField(
value = userName.value,
onValueChange = {
userName.value = it
},
maxLines = 1
)
}
},
confirmButton = {
TextButton(onClick = {
openDialog.value = false
Toast.makeText(context, "saving..", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
val record = ScoreContract.Record(
viewState.score,
System.currentTimeMillis(),
userName.value
)
dbHelper.insertScore(record)
}) {
Text("Save")
}
},
dismissButton = {
TextButton(onClick = {
openDialog.value = false
}
) {
Text("Don't Save")
}
}
)
} else {
viewModel.reset()
}
}
preview 的效果如下
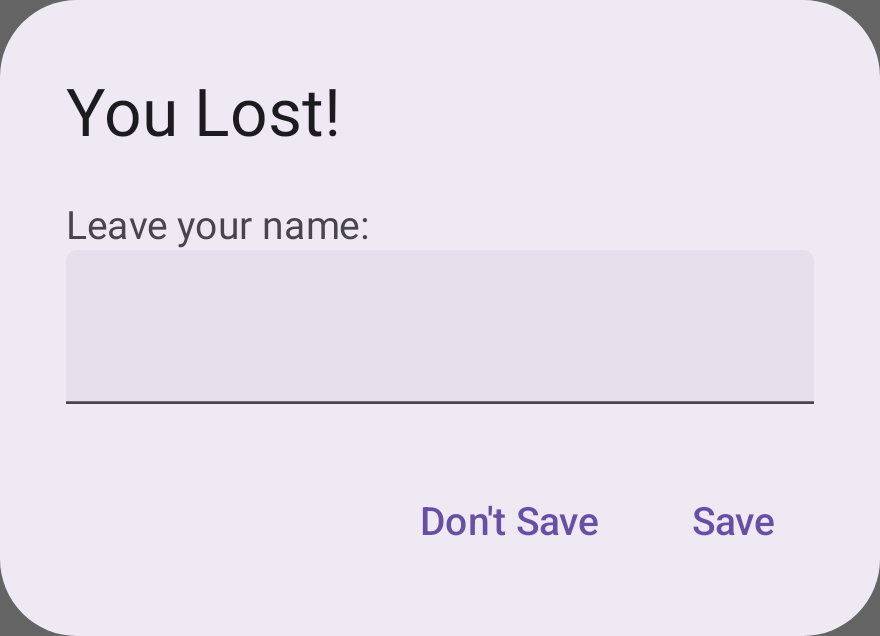
在 text 中组合一个 TextField 用于输入名字,用一个 mutableState 来维护名字。存储的时候,在 onClick 方法中插入数据库
openDialog.value = false
Toast.makeText(context, "saving..", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
val record = ScoreContract.Record(
viewState.score,
System.currentTimeMillis(),
userName.value
)
dbHelper.insertScore(record)
这里没有搞协程来做,因为懒。
然后是数据库操作,参考着谷歌的文档,首先搞个 contract
object ScoreContract {
object ScoreEntry : BaseColumns {
const val TABLE_NAME = "TetrisScore"
const val COLUMN_TIME = "time"
const val COLUMN_NAME = "name"
const val COLUMN_SCORE = "score"
}
data class Record(val score : Int, val currentTimeMillis : Long, val name : String)
}
然后实现 dbHelper
class ScoreDBHelper(context: Context) : SQLiteOpenHelper(context, DATABASE_NAME, null, DATABASE_VERSION){
private val SQL_CREATE_ENTRYS =
"CREATE TABLE ${ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.TABLE_NAME} (" +
"${ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_TIME} INTEGER PRIMARY KEY," +
"${ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_NAME} TEXT," +
"${ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_SCORE} INTEGER)"
private val SQL_DELETE_ENTRYS = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS ${ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.TABLE_NAME}"
override fun onCreate(p0: SQLiteDatabase) {
p0.execSQL(SQL_CREATE_ENTRYS)
}
override fun onUpgrade(p0: SQLiteDatabase, p1: Int, p2: Int) {
p0.execSQL(SQL_DELETE_ENTRYS)
onCreate(p0)
}
override fun onDowngrade(db: SQLiteDatabase, oldVersion: Int, newVersion: Int) {
onUpgrade(db, oldVersion, newVersion)
}
fun insertScore(record : ScoreContract.Record) {
val db = writableDatabase
val values = ContentValues().apply {
put(ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_SCORE, record.score)
put(ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_TIME, record.currentTimeMillis)
put(ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_NAME, record.name)
}
db.insert(ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.TABLE_NAME, null, values)
db.close()
}
private fun rawSearch(selection : String) : MutableList<ScoreContract.Record> {
val db = writableDatabase
try {
val cursor = db.query(
ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.TABLE_NAME,
null,
selection,
null,
null,
null,
null
)
val records = mutableListOf<ScoreContract.Record>()
with(cursor) {
while (moveToNext()) {
val record = ScoreContract.Record(
getInt(getColumnIndexOrThrow(ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_SCORE)),
getLong(getColumnIndexOrThrow(ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_TIME)),
getString(getColumnIndexOrThrow(ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_NAME))
)
records.add(record)
}
}
return records
} catch (e : SQLiteException) {
db.close()
return mutableListOf()
}
}
fun searchScoreByName(name : String) : MutableList<ScoreContract.Record> {
val selection = "${ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_NAME} = \"$name\""
return rawSearch(selection)
}
fun searchScoreByTime(start : Long, end : Long) : MutableList<ScoreContract.Record> {
val selection = "${ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_TIME} <= $end and " +
"${ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_TIME} >= $start"
return rawSearch(selection)
}
fun selectAll() : List<ScoreContract.Record> {
val selection = "SELECT * FROM ${ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.TABLE_NAME}"
val db = writableDatabase
try {
val cursor = db.rawQuery(selection, null)
val records = mutableListOf<ScoreContract.Record>()
with(cursor) {
while (moveToNext()) {
val record = ScoreContract.Record(
getInt(getColumnIndexOrThrow(ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_SCORE)),
getLong(getColumnIndexOrThrow(ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_TIME)),
getString(getColumnIndexOrThrow(ScoreContract.ScoreEntry.COLUMN_NAME))
)
records.add(record)
}
}
return records
} catch (e : SQLiteException) {
db.close()
return mutableListOf()
}
}
companion object {
const val DATABASE_NAME = "tetris_score"
const val DATABASE_VERSION = 1
}
}
这里面实现了朴素的查询插入方法。
存储就这么解决了。
分数显示
为了显示分数,自然的想法是用一个 list 显示出来,在传统的 view 系统里面,有 LIstView 和 RecycleView,compose 中则类似的,有 Column 和 LazyColumn,如此即可
@Composable
fun ScoreList(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
val viewModel = viewModel<ScoreSearchViewModel>()
val viewState = viewModel.viewState
val records = remember { mutableStateListOf<ScoreContract.Record>() }
records.clear()
records.addAll(viewState.value.records)
LazyColumn(
modifier = modifier,
) {
items(records) { record ->
ScoreItem(score = record, modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.height(60.dp))
}
}
}
他会自动根据 modifier 显示出对应大小的区域,滚动时也会自动刷新,比起 RecycleView 要实现一个 adapter 来说,要方便许多。
然后单个分数,compose 一个框就行了
@Preview(showBackground = true)
@Composable
@SuppressLint("SimpleDateFormat")
fun ScoreItem(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
score : ScoreContract.Record = ScoreContract.Record(100, 1653213538, "chuj")
) {
val gradientBrush = Brush.horizontalGradient(
colors = listOf(Color.Red, Color.Blue, Color.Green),
)
Column(
modifier = modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.border(
brush = gradientBrush,
width = 2.dp,
shape = CircleShape
),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceBetween
) {
Row(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(),
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically,
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceAround
) {
Text(
text = score.name,
fontSize = 22.sp
)
Text(
text = score.score.toString(),
fontSize = 20.sp,
)
}
Text(text = SimpleDateFormat("yy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss").format(score.currentTimeMillis))
}
}
预览出来是这样的效果

嗯,看起来效果很差,主要是 Modifer.fillMaxSize 了,占满了整个屏幕,之后调用的时候会限制大小,效果还是可以的。
这个彩色的渐变也是通过 brush 来的,挺有意思的。
显示分数我是实现了一个新的 activity 专门实现(实际上 compose 的时候,并不需要用多 activity,可以通过 mutableState 来直接 switch 多个屏幕,实现 activity 的效果。为什么我没这么做呢,emmm,好问题)。这里我也新弄了一个 viewModel 来做,
class ScoreSearchViewModel : ViewModel() {
private val _viewState = mutableStateOf(ScoreSearchViewState())
val viewState : State<ScoreSearchViewState> = _viewState
private fun reduce(newViewState: ScoreSearchViewState) {
_viewState.value = newViewState
}
fun reduceSearchAlert(onSearchAlert: Boolean) {
reduce(viewState.value.copy(onSearchAlert = onSearchAlert))
}
fun reduceRecords(records: List<ScoreContract.Record>) {
reduce(viewState.value.copy(
records = records,
recordsWasSet = true,
))
}
fun reduceSearchTime(
timeStart : Long = viewState.value.searchTimeStart,
timeEnd : Long = viewState.value.searchTimeEnd
) {
_viewState.value = viewState.value.copy(
searchTimeEnd = timeEnd,
searchTimeStart = timeStart
)
}
}
data class ScoreSearchViewState (
val records: List<ScoreContract.Record> = emptyList(),
val searchTimeStart : Long = 0L,
val searchTimeEnd : Long = 0L,
val onSearchAlert : Boolean = false,
val recordsWasSet : Boolean = false,
)
*最后没用上这个 searchTimeStart 和 searchTimeEnd,因为整个搜索都在之后的 alertDialog 里面实现了,实际上违反了单向数据流,对于用户的输入在 View 层内解决了,Intent 变成了 records。不过懒得重构了。
@Preview(showBackground = true)
@Composable
@SuppressLint("SimpleDateFormat")
fun SearchAlert() {
val context = LocalContext.current
var searchType by remember { mutableStateOf(SearchType.OnDeciding)}
val viewModel = viewModel<ScoreSearchViewModel>()
val viewState = viewModel.viewState
val dbHelper = ScoreDBHelper(context)
var searchName by remember { mutableStateOf("") }
var timeSetState by remember { mutableStateOf(TimeSetState.OnInit) }
var timeInput by remember { mutableStateOf("00:00") }
var dateInput by remember { mutableStateOf("2000/01/01") }
val currentStartYear = dateInput.subSequence(0, 4).toString().toInt()
val currentStartMonth = dateInput.subSequence(5, 7).toString().toInt()
val currentStartDay = dateInput.subSequence(8, 10).toString().toInt()
val currentStartHour = timeInput.subSequence(0, 2).toString().toInt()
val currentStartMinute = timeInput.subSequence(3, 5).toString().toInt()
val timePickerDialog = TimePickerDialog(
context,
{_, hour : Int, minute : Int ->
timeInput = "${hour.toString().padStart(2, '0')}:${minute.toString().padStart(2, '0')}"
}, currentStartHour, currentStartMinute, false
)
val datePickerDialog = DatePickerDialog(
context,
{_, year : Int, month : Int, dayOfMonth : Int ->
dateInput = "$year/${(month + 1).toString().padStart(2, '0')}/${dayOfMonth.toString().padStart(2, '0')}"
}, currentStartYear, currentStartMonth, currentStartDay
)
var searchStartTime by remember { mutableStateOf(0L) }
var searchEndTime by remember { mutableStateOf(0L) }
val timeToParse = "$dateInput $timeInput"
println("[!] $timeToParse")
if (timeSetState == TimeSetState.OnSetStartTime || timeSetState == TimeSetState.OnInit) {
searchStartTime = SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm").parse(timeToParse).time
println("[+] start time set $searchStartTime")
}
if (timeSetState == TimeSetState.OnSetEndTime || timeSetState == TimeSetState.OnInit) {
searchEndTime = SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm").parse(timeToParse).time
println("[+] end time set $searchStartTime")
}
if (viewState.value.onSearchAlert) {
when(searchType) {
SearchType.OnDeciding -> AlertDialog(
onDismissRequest = { viewModel.reduceSearchAlert(false) },
title = {
Text(text = "Search")
},
text = {
Text(text = "What you want to search by?")
},
confirmButton = {
TextButton(
onClick = { searchType = SearchType.ByName }
) {
Text(text = "By Name")
}
},
dismissButton = {
TextButton(
onClick = { searchType = SearchType.ByTime }
) {
Text(text = "By Time")
}
}
)
SearchType.ByTime -> AlertDialog(
onDismissRequest = { viewModel.reduceSearchAlert(false) },
title = {
Text(text = "Search By Time")
},
text = {
Row(
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceAround,
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically
) {
ClickableText(
text = AnnotatedString(SimpleDateFormat("yy/MM/dd ")
.format(searchStartTime)),
onClick = {
timeSetState = TimeSetState.OnSetStartTime
datePickerDialog.show()
}
)
ClickableText(
text = AnnotatedString(SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm")
.format(searchStartTime)),
onClick = {
timeSetState = TimeSetState.OnSetStartTime
timePickerDialog.show()
}
)
Text(
text = " To "
)
ClickableText(
text = AnnotatedString(SimpleDateFormat("yy/MM/dd ")
.format(searchEndTime)),
onClick = {
timeSetState = TimeSetState.OnSetEndTime
datePickerDialog.show()
}
)
ClickableText(
text = AnnotatedString(SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm")
.format(searchEndTime)),
onClick = {
timeSetState = TimeSetState.OnSetEndTime
timePickerDialog.show()
}
)
}
},
confirmButton = {
TextButton(onClick = {
val records = dbHelper.searchScoreByTime(searchStartTime, searchEndTime)
viewModel.reduceRecords(records = records)
viewModel.reduceSearchAlert(false)
}) {
Text(text = "Search!")
}
},
dismissButton = {
TextButton(onClick = { viewModel.reduceSearchAlert(false) }) {
Text(text = "Cancel")
}
}
)
SearchType.ByName -> AlertDialog(
onDismissRequest = { viewModel.reduceSearchAlert(false) },
title = {
Text(text = "Search By Name")
},
text = {
Text(text = "Enter a name")
TextField(
value = searchName,
onValueChange = {
searchName = it
}
)
},
confirmButton = {
TextButton(onClick = {
val records = dbHelper.searchScoreByName(name = searchName)
viewModel.reduceRecords(records = records)
viewModel.reduceSearchAlert(false)
}) {
Text(text = "Search!")
}
},
dismissButton = {
TextButton(onClick = { viewModel.reduceSearchAlert(false) }) {
Text(text = "Cancel")
}
}
)
}
}
}
这就是整个搜索的 dialog。在 compose 中还没有 Material Design 的 time 和 date picker,查了点资料发现了 DatePickerDialog 和 TimePickerDialog,感觉长得挺像 Material Design 的,我也不知道是什么,anyway,用起来比较容易
val timePickerDialog = TimePickerDialog(
context,
{_, hour : Int, minute : Int ->
timeInput = "${hour.toString().padStart(2, '0')}:${minute.toString().padStart(2, '0')}"
}, currentStartHour, currentStartMinute, false
)
val datePickerDialog = DatePickerDialog(
context,
{_, year : Int, month : Int, dayOfMonth : Int ->
dateInput = "$year/${(month + 1).toString().padStart(2, '0')}/${dayOfMonth.toString().padStart(2, '0')}"
}, currentStartYear, currentStartMonth, currentStartDay
)
第二个参数就是一个 listener 了,在这里根据输入更新相关的变量即可。
播放音乐
挂了之后要放个小曲,本来是想在失败动画的协程中放的,也就是这里面
viewModelScope.launch {
(0 until viewState.value.grid.second).reversed().forEach { y ->
delay(120)
// A. create black bricks
val brickLine = mutableListOf<Brick>()
(0 until viewState.value.grid.first).forEach { x ->
brickLine.add(Brick(Offset(x.toFloat(), y.toFloat()), Color.Black))
}
val bricks = _viewState.value.bricks.toMutableList()
bricks.addAll(brickLine)
_viewState.value = _viewState.value.copy(
bricks = bricks
)
}
_viewState.value = _viewState.value.copy(gameStatus = GameStatus.GameOver)
}
但是我拿不到 context,起不来,没搞懂,可能音乐播放不应该在这里面做,最后我给 state 加了 onGameOverAnimation 状态,在持续发送下落的 game ticking 协程里面才起了 mediaPlay,也就是
LaunchedEffect(key1 = Unit) {
var musicPlaying = false
while (true) {
delay(
450 - min(viewState.linesCleared.toLong() * 10, 250)
)
viewModel.dispatch(Action.Tick)
if (!musicPlaying && viewModel.viewState.value.isOnGameOverAnimation) {
musicPlaying = true
val lostMusicPlayer = MediaPlayer.create(context, R.raw.on_lost_animation_music)
lostMusicPlayer.start()
}
}
}
最后
好了,到这里差不多就结束了。前前后后可能花了三四十个小时写这个项目(还不包括查资料的时间)。幸运的是,学到了许多知识。之前一直在弄安全,二进制安全其实是比较偏向底层的,很多时候可能并不会关心宏观的架构,只会深入研究一个子模块,而且在开发方面的经验也是比较少。通过这个项目,受着 MVI 的指导,踩着谷歌 jetpack compose 的大火箭,感受了便捷开发的快乐。也是把以前学的抽象的设计模式用到了实际的工程中。收获颇多,非常开心hhh。
文章写的比较简略,等我过段时间再来看看,发现我看不懂了的话就再补充一点